SWOT analysis tool - toolthinker.com
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is SWOT analysis?
In the realm of strategic planning and decision-making, organizations rely on various tools and frameworks to assess their current standing and chart a course for future success. One such widely used and powerful tool is SWOT analysis. Whether you’re an entrepreneur, a manager, or a student of business, understanding SWOT analysis can provide valuable insights into assessing internal strengths, weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats.
SWOT analysis is an acronym that stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is a structured approach that enables individuals and organizations to evaluate their current position in relation to their competition, industry trends, and overall market dynamics. By identifying and analyzing these four critical components, organizations can gain valuable insights to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the core concepts of SWOT analysis, explore the benefits it offers, and discuss how it can be applied in various contexts. We will walk you through each element of SWOT analysis, providing practical examples and guidelines to ensure you have a solid understanding of this powerful tool.
By the end of this article, you will not only grasp the fundamentals of SWOT analysis but also gain the necessary knowledge to conduct your own SWOT analysis effectively. So, let’s dive in and unravel the world of SWOT analysis, uncovering its potential to unlock strategic advantages and drive organizational success.
What is the history of SWOT analysis?
SWOT analysis, a widely used strategic planning tool, has a history dating back several decades. It is believed to have originated in the 1960s as a result of research conducted at the Stanford Research Institute (now SRI International) in California, USA. During this time, Albert Humphrey and his team developed a framework known as SOFT analysis (an acronym for Satisfactory, Opportunity, Fault, and Threat) to assess corporate planning processes.
Over time, the framework evolved into the widely recognized SWOT analysis we know today. The acronym was later modified to include Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats, aligning with the core components of the analysis. SWOT analysis gained popularity in the business world during the 1970s and 1980s as a tool for evaluating organizations’ internal capabilities and external environment. It provided a structured approach to assess strategic positions, identify areas for improvement, and capitalize on market opportunities.
Since its inception, SWOT analysis has become a fundamental tool in strategic planning, marketing, and decision-making processes across various industries. Its simplicity and versatility make it accessible to organizations of all sizes, ranging from small businesses to large multinational corporations. Today, SWOT analysis continues to be an essential tool in assessing organizations’ current state, identifying potential avenues for growth, and managing risks and challenges in an ever-changing business landscape.
What are the four components of SWOT analysis?
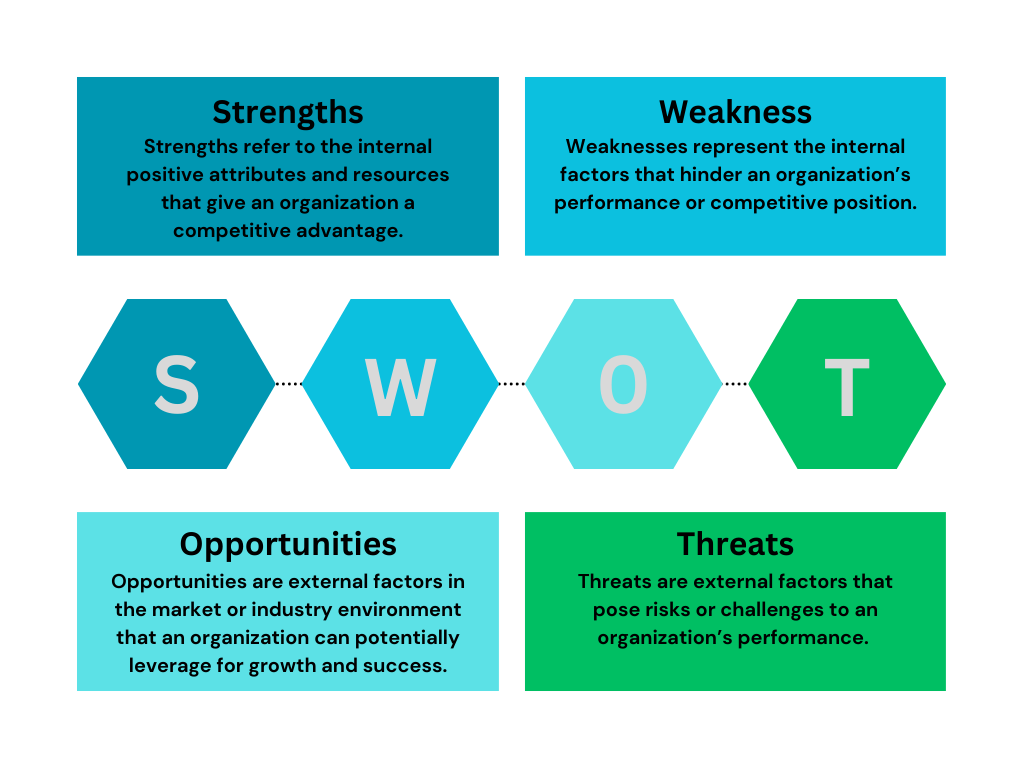
SWOT analysis consists of four essential components, each representing a distinct aspect of an organization’s internal and external environment. These components are:
Strengths
Strengths refer to the internal positive attributes and resources that give an organization a competitive advantage. They can include factors such as a strong brand reputation, skilled workforce, unique products or services, efficient processes, or strong customer loyalty. Identifying strengths helps organizations understand their core capabilities and areas of excellence.
Weaknesses
Weaknesses represent the internal factors that hinder an organization’s performance or competitive position. These can include aspects such as limited financial resources, outdated technology, poor customer service, ineffective marketing strategies, or high employee turnover. Recognizing weaknesses allows organizations to address and improve upon areas that need development.
Opportunities
Opportunities are external factors in the market or industry environment that an organization can potentially leverage for growth and success. These can arise from market changes, emerging technologies, new customer segments, partnerships, or favorable economic conditions. Identifying opportunities enables organizations to capitalize on favorable circumstances and gain a competitive edge.
Threats
Threats are external factors that pose risks or challenges to an organization’s performance. They can include intense competition, changing regulations, economic downturns, shifts in consumer preferences, or technological disruptions. Recognizing threats helps organizations proactively mitigate or prepare for potential challenges, ensuring long-term sustainability.
By analyzing these four components comprehensively, organizations can develop a holistic understanding of their current situation and make informed decisions. Assessing strengths and weaknesses provides insights into the internal aspects that need to be capitalized upon or improved, while recognizing opportunities and threats allows organizations to navigate the external landscape strategically.
It is important to note that these four components are interconnected and influence each other. Strengths can be utilized to seize opportunities, weaknesses can be addressed to mitigate threats, and both strengths and weaknesses can impact how an organization responds to external factors.
A well-executed SWOT analysis considers all four components and their interplay, enabling organizations to align their strategies, allocate resources effectively, and stay competitive in a dynamic business environment.
How does SWOT analysis work?
SWOT analysis works by systematically evaluating an organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. This evaluation helps to create a comprehensive snapshot of the organization’s current situation and enables informed decision-making. The process of conducting a SWOT analysis typically involves the following steps:
Identifying Strengths
The first step is to identify the internal strengths of the organization. These are the positive attributes and resources that give the organization a competitive advantage over others. Strengths can include factors such as a strong brand reputation, skilled workforce, unique products or services, efficient processes, or strong customer loyalty. It is crucial to be honest and realistic while identifying strengths to ensure accuracy.
Recognizing Weaknesses
The next step is to assess the internal weaknesses of the organization. These are the areas where the organization lacks a competitive edge or faces challenges. Weaknesses can include factors such as limited financial resources, outdated technology, poor customer service, ineffective marketing strategies, or high employee turnover. Identifying weaknesses allows organizations to address and improve upon them.
Exploring Opportunities
After assessing internal factors, it’s important to analyze the external environment for potential opportunities. Opportunities are favorable circumstances or trends that could be beneficial to the organization. These can arise from market changes, emerging technologies, new customer segments, partnerships, or favorable economic conditions. Identifying opportunities enables organizations to capitalize on them and gain a competitive edge.
Evaluating Threats
The final step involves examining external threats that could negatively impact the organization. Threats are factors in the external environment that could hinder the organization’s performance or pose risks. They can include intense competition, changing regulations, economic downturns, shifts in consumer preferences, or technological disruptions. Recognizing threats helps organizations proactively mitigate or prepare for potential challenges.
Once the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats have been identified, the next crucial step is to analyze and prioritize them. This involves assessing the significance of each factor and determining their impact on the organization’s goals and objectives. Prioritizing helps in developing strategies to leverage strengths, overcome weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate threats.
It’s important to note that SWOT analysis is not a one-time activity. The business landscape is dynamic, and factors can change over time. Therefore, organizations should regularly review and update their SWOT analysis to ensure its relevance and effectiveness in guiding strategic decision-making.
By following the systematic process of SWOT analysis, organizations can gain valuable insights into their current situation, assess their competitive position, and develop strategies that capitalize on strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate threats. SWOT analysis serves as a foundation for informed decision-making and strategic planning, enabling organizations to navigate challenges and achieve their objectives successfully.
What are the benefits of conducting a SWOT analysis?
Conducting a SWOT analysis offers several valuable benefits to individuals and organizations. Some of the key advantages include:
Enhanced Strategic Planning
A SWOT analysis provides a structured framework for strategic planning. By assessing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, organizations gain a comprehensive understanding of their current situation. This insight helps in developing well-informed strategies that leverage strengths, address weaknesses, and capitalize on opportunities, while mitigating threats.
Improved Decision-making
SWOT analysis enables informed decision-making by providing a holistic view of the internal and external factors affecting an organization. It helps in identifying potential risks, uncovering growth opportunities, and aligning decisions with the organization’s capabilities and goals. With a clear understanding of the SWOT components, decision-makers can make more effective choices.
Identifying Competitive Advantages
Through a SWOT analysis, organizations can identify their unique strengths and competitive advantages. These strengths could be in the form of specialized expertise, superior customer service, advanced technology, or strong brand recognition. Understanding these advantages allows organizations to differentiate themselves in the market and gain a competitive edge.
Risk Mitigation
SWOT analysis helps in recognizing and assessing potential threats and risks that an organization may face. By understanding these threats, organizations can develop strategies to mitigate their impact and proactively prepare for challenges. This allows for better risk management and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
Resource Allocation
SWOT analysis helps organizations allocate their resources effectively. By identifying strengths and opportunities, organizations can allocate resources to areas that offer the most potential for growth and success. Similarly, by addressing weaknesses and mitigating threats, organizations can allocate resources to areas that require improvement or risk management.
Communication and Collaboration
SWOT analysis promotes communication and collaboration within organizations. It encourages stakeholders to come together, share insights, and contribute their perspectives. This collaborative approach fosters a better understanding of the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, leading to more effective teamwork and decision-making.
Overall, conducting a SWOT analysis allows organizations to gain a comprehensive understanding of their internal and external environment, identify key factors influencing their success, and develop strategies to leverage strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate threats. By leveraging these benefits, organizations can enhance their competitiveness, make informed decisions, and achieve their strategic objectives.
How do I conduct a SWOT analysis?
Conducting a SWOT analysis involves a systematic approach to assess an organization’s internal strengths, weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. Start by gathering relevant information about your organization, such as financial reports, performance data, customer feedback, and market research. Then, brainstorm and identify the key factors for each component of the SWOT analysis. Assess the strengths and weaknesses by critically evaluating your organization’s resources, capabilities, and areas for improvement. For opportunities and threats, analyze the external environment, market trends, competition, and any potential risks or challenges. Finally, prioritize the findings based on their significance and develop strategies that leverage strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate threats.
Can SWOT analysis be used for personal development?
Yes, SWOT analysis can be a valuable tool for personal development. Start by assessing your personal strengths, such as skills, knowledge, and personal attributes that give you an advantage. Next, identify your weaknesses or areas where you need improvement. This self-awareness allows you to focus on personal growth and development opportunities.
Additionally, explore the external environment for opportunities, such as networking events, educational programs, or career advancements that align with your goals. Finally, recognize potential threats or challenges that may hinder your progress and develop strategies to overcome them. By conducting a SWOT analysis for personal development, you can gain insights into your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and make informed decisions to enhance your personal and professional life.
What is the difference between internal and external factors in a SWOT analysis?
In a SWOT analysis, internal factors refer to the characteristics and resources within an organization that have an impact on its performance. These factors are under the organization’s control and include aspects such as the company’s culture, human resources, financial stability, operational efficiency, and proprietary technology or intellectual property. Internal factors are assessed to identify an organization’s strengths and weaknesses, which provide insights into its core competencies and areas that need improvement.
On the other hand, external factors are the elements outside the organization’s direct control but still influence its operations and success. These factors arise from the broader business environment, including market conditions, industry trends, regulatory changes, economic factors, technological advancements, and competitive landscape. External factors are evaluated to identify opportunities that can be leveraged and threats that may pose risks or challenges to the organization. Understanding external factors allows organizations to adapt their strategies, capitalize on market trends, and navigate potential obstacles.
How do I prioritize the findings of a SWOT analysis?
Prioritizing the findings of a SWOT analysis involves assessing the significance and impact of each identified factor. One approach is to use a prioritization matrix or grid. Assign a numerical or qualitative rating to each factor based on its importance and potential influence on the organization. Consider factors such as the potential for growth, competitiveness, feasibility of addressing weaknesses, or the potential impact of threats. By ranking the factors based on their ratings, you can identify the most critical and impactful ones.
Another approach is to conduct a brainstorming session or a group discussion with key stakeholders to gather their perspectives and insights. This collaborative effort can help identify shared priorities and ensure a well-rounded evaluation of the factors. It is important to remember that prioritization is subjective and can vary based on the organization’s goals, current situation, and available resources. Therefore, it is essential to align the prioritization process with the specific objectives and context of the organization.
By prioritizing the findings of a SWOT analysis, organizations can focus their attention, resources, and strategies on the most critical areas that will have the greatest impact on their success.
Are there any potential pitfalls or limitations of SWOT analysis?
While SWOT analysis is a valuable tool, it is important to be aware of its potential pitfalls and limitations. One limitation is that SWOT analysis provides a snapshot of the current situation, and it may not capture the dynamic nature of the business environment. Factors can change rapidly, and the analysis may not reflect emerging trends or unforeseen events. Therefore, it is crucial to regularly review and update the SWOT analysis to ensure its relevance.
Another pitfall is the tendency to overlook or dismiss certain factors. Biases or preconceived notions can influence the evaluation process, leading to an incomplete or skewed analysis. To mitigate this, it is essential to encourage diverse perspectives, engage multiple stakeholders, and foster an open and objective discussion during the analysis.
Additionally, SWOT analysis may lack specificity and fail to provide detailed actionable insights. While it helps identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, it does not prescribe specific strategies or implementation plans. To overcome this limitation, organizations should follow up the SWOT analysis with more detailed planning and execution processes.
By understanding these potential pitfalls and limitations, organizations can approach SWOT analysis with a critical mindset and use it as a starting point for further analysis and decision-making.
Can SWOT analysis be applied to different industries or sectors?
Yes, SWOT analysis can be applied to different industries or sectors. Its versatility lies in the fact that it is a framework that can be adapted to suit various contexts. Whether it’s a manufacturing company, a service-oriented business, a nonprofit organization, or even an individual’s personal development, SWOT analysis can be a valuable tool.
The key is to tailor the analysis to the specific industry or sector by considering relevant factors. For example, in a healthcare industry SWOT analysis, factors like regulatory compliance, technological advancements, patient satisfaction, or healthcare policies may be crucial considerations. On the other hand, in a retail industry SWOT analysis, factors like consumer trends, supply chain management, competitive pricing, or online presence may take precedence.
By customizing the SWOT analysis to the specific industry or sector, organizations can gain industry-specific insights and make informed decisions that are relevant to their unique circumstances and challenges.
How can SWOT analysis help with business growth and expansion?
SWOT analysis can be instrumental in guiding business growth and expansion strategies. By assessing the organization’s internal strengths, it identifies areas where the business has a competitive advantage and can leverage those strengths to pursue growth opportunities. It helps organizations capitalize on their unique capabilities, resources, and expertise to gain a competitive edge in the market.
Furthermore, SWOT analysis helps in identifying and addressing weaknesses or limitations that could hinder growth initiatives. By understanding these weaknesses, organizations can develop strategies to improve operational efficiency, enhance product offerings, or invest in necessary resources or talent to overcome obstacles.
The analysis also facilitates the identification of external opportunities that align with the organization’s growth objectives. It allows businesses to stay proactive in identifying emerging market trends, potential partnerships, new customer segments, or untapped geographic markets. By recognizing these opportunities, organizations can develop strategies to exploit them and expand their market reach.
Additionally, SWOT analysis helps businesses evaluate potential threats or challenges that may arise during the growth and expansion process. It enables them to assess market competition, changing consumer behaviors, regulatory risks, or economic factors that could impact their growth plans. By understanding these threats, organizations can develop contingency plans and mitigate risks.
Overall, SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s internal and external factors, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning for business growth and expansion.
SWOT analysis example
Here’s an example of a SWOT analysis for a fictional retail company:
Strengths:
-
- Strong brand recognition and customer loyalty.
-
- Wide range of high-quality products and competitive pricing.
-
- Well-established distribution network and efficient supply chain management.
-
- Skilled and knowledgeable sales team.
-
- Robust online presence and e-commerce capabilities.
Weakness:
-
- Limited geographic presence, with most stores concentrated in specific regions.
-
- Relatively higher overhead costs compared to some competitors.
-
- Inconsistent customer service experiences across different store locations.
-
- Limited product differentiation in certain categories.
-
- Reliance on a few key suppliers for certain product lines.
Opportunities:
-
- Growing demand for online shopping and e-commerce.
-
- Expansion into new geographic markets and opening additional store locations.
-
- Diversification of product offerings to cater to emerging trends and customer preferences.
-
- Collaborations with popular influencers or brand ambassadors to enhance brand visibility.
-
- Integration of new technologies, such as mobile apps or virtual reality, to enhance the shopping experience.
Threats:
-
- Intense competition from both traditional retailers and e-commerce giants.
-
- Economic downturns impacting consumer spending habits.
-
- Increasing costs of raw materials and potential supply chain disruptions.
-
- Changing consumer preferences and trends that may require rapid adaptation.
-
- Potential regulatory changes affecting the retail industry, such as taxation or trade policies.
This example provides an overview of the company’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. By analyzing these factors, the company can develop strategies to leverage its strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate threats in order to remain competitive and achieve sustainable growth.
SWOT Analysis Tools
There are several SWOT analysis tools and templates available that can assist in conducting a SWOT analysis. Here are a few commonly used ones:
Grid or Matrix Template
The grid or matrix template is the most common and straightforward tool for conducting a SWOT analysis. It involves creating a four-quadrant table with sections for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This template allows for easy visualization and organization of the analysis.
TOWS Matrix
The TOWS matrix is an extension of the traditional SWOT analysis. It helps in developing strategic options by combining internal strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats. The matrix helps to identify potential strategies that align strengths with opportunities, address weaknesses to seize opportunities, minimize weaknesses in the face of threats, or defend against threats leveraging strengths.
PESTEL Analysis
While not a specific SWOT tool, PESTEL analysis is often used in conjunction with SWOT analysis. PESTEL stands for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors. This analysis helps to assess the external macro-environmental factors that influence an organization. By conducting a PESTEL analysis alongside a SWOT analysis, a more comprehensive understanding of the external environment can be achieved.
SWOT Analysis Software
Various software applications and online tools are available that facilitate the process of conducting a SWOT analysis. These tools often provide pre-designed templates, collaboration features, and additional analytical capabilities to streamline the process and enhance the visual representation of the analysis.
When selecting a SWOT analysis tool, it’s important to consider the specific needs of your organization, the level of detail required, and the preferred format for presenting the analysis. The chosen tool should align with the goals and objectives of the analysis and support the decision-making process effectively.