In today’s dynamic business environment, staying ahead requires more than just understanding your organization and its internal processes. External factors can significantly impact business performance and strategic planning. This is where the PEST Analysis framework becomes invaluable. By systematically evaluating Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors, PEST Analysis provides a comprehensive picture of the macro-environment in which a business operates.
This blog delves into the PEST Analysis framework, exploring its components, benefits, practical applications, and tips for implementation.
What is PEST Analysis?
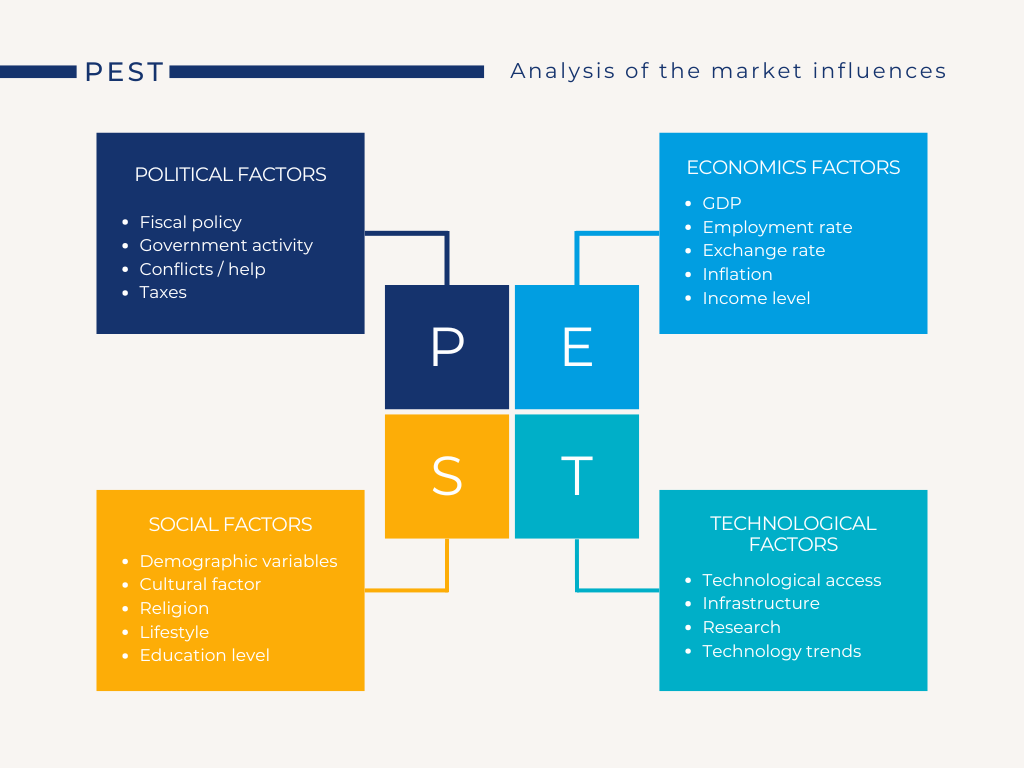
PEST Analysis is a strategic framework used to identify and analyze the key macro-environmental factors that influence an organization. The acronym PEST stands for:
- Political: Government policies, regulations, and political stability.
- Economic: Market conditions, economic trends, and financial factors.
- Social: Cultural and societal trends, demographics, and consumer behavior.
- Technological: Technological advancements, innovation, and R&D trends.
By examining these four categories, businesses can anticipate external opportunities and threats, enabling better strategic planning and decision-making.
The Four Pillars of PEST Analysis
1. Political Factors
Political factors include government policies, political stability, tax regulations, trade restrictions, and labor laws. These elements can shape the business landscape and affect operations. For example:
- Changes in tax policies can influence business profitability.
- Political instability can deter investment in certain regions.
- Trade restrictions or tariffs may impact supply chains and market access.
Example: The Brexit decision in the UK significantly altered trade regulations and economic relationships, prompting companies to reassess their operations in Europe.
2. Economic Factors
Economic factors pertain to the broader financial environment affecting businesses. These include:
- Inflation rates, interest rates, and exchange rates.
- Unemployment levels and consumer spending habits.
- Economic growth or recession cycles.
Understanding these elements helps businesses forecast market conditions and plan accordingly. For instance:
- High inflation may increase operational costs.
- Favorable exchange rates can make exporting goods more profitable.
Example: During the COVID-19 pandemic, economic downturns and shifts in consumer behavior required businesses to pivot their strategies rapidly.
3. Social Factors
Social factors focus on cultural norms, values, demographics, and consumer behavior. These insights help businesses align products and services with societal trends. Key areas to assess include:
- Population demographics (age, gender, income levels).
- Health consciousness, environmental awareness, and lifestyle changes.
- Consumer attitudes and purchasing behaviors.
Example: The rise of environmental awareness has driven demand for sustainable products and eco-friendly packaging.
4. Technological Factors
Technological factors encompass innovations, advancements, and the rate of technological change. These can open new markets, improve efficiency, or disrupt industries. Key considerations include:
- Emerging technologies (e.g., AI, blockchain, IoT).
- Investment in research and development (R&D).
- Technological infrastructure and digital transformation.
Example: The widespread adoption of e-commerce platforms like Amazon and Shopify revolutionized retail and forced traditional stores to adapt to digital marketplaces.
Benefits of PEST Analysis
PEST Analysis offers several advantages, making it a crucial tool for businesses:
- Strategic Insight: Identifies external opportunities and threats.
- Risk Mitigation: Helps businesses anticipate challenges and develop contingency plans.
- Market Understanding: Provides a clear view of macro-environmental trends influencing industries.
- Informed Decision-Making: Improves the quality of strategic planning and investments.
How to Conduct a PEST Analysis
Conducting a PEST Analysis involves a step-by-step approach:
- Define the Objective Start by clarifying what you aim to achieve. Are you analyzing a specific market, launching a new product, or entering a new region?
- Gather Relevant Data Use credible sources such as government reports, industry analyses, and market research to collect information on political, economic, social, and technological factors.
- Analyze Each Factor Examine how each PEST component impacts your business or project. For example:
- Are there upcoming regulations that could affect your operations?
- How is consumer behavior evolving in your target market?
- Identify Key Takeaways Highlight the most significant findings and prioritize them based on their potential impact.
- Incorporate Findings into Strategy Use the insights from your PEST Analysis to adjust your business strategy. This might involve diversifying markets, investing in technology, or modifying your product offerings.
Practical Example of PEST Analysis
Imagine a company planning to expand its operations into a new international market. Here’s how a PEST Analysis might look for this scenario:
Political Factors
- Political stability in the target market.
- Trade agreements between the home country and the target market.
- Tax incentives for foreign businesses.
Economic Factors
- Economic growth rate and disposable income levels in the region.
- Currency exchange rates impacting profitability.
- Local labor market conditions and wage expectations.
Social Factors
- Cultural preferences and consumer expectations.
- Demographics and population trends.
- Social attitudes toward foreign brands.
Technological Factors
- Availability of digital infrastructure.
- Adoption rates of technology in the target market.
- Opportunities for leveraging innovative technologies like mobile apps.
By analyzing these factors, the company can make informed decisions about whether and how to enter the market.
Challenges and Limitations of PEST Analysis
While PEST Analysis is a powerful tool, it has some limitations:
- Subjectivity: The quality of insights depends on the analyst’s interpretation and expertise.
- Dynamic Nature: External factors can change rapidly, requiring frequent updates to the analysis.
- Interdependencies: Overlaps between PEST factors (e.g., political decisions impacting the economy) can complicate analysis.
To overcome these challenges, businesses should regularly update their PEST Analysis and complement it with other frameworks, such as SWOT Analysis or Porter’s Five Forces.
Integrating PEST Analysis with Framework Thinking
PEST Analysis is most effective when used as part of a broader strategic toolkit. For instance:
- Combine PEST Analysis with SWOT Analysis to identify internal strengths and weaknesses alongside external opportunities and threats.
- Use Porter’s Five Forces to assess competitive pressures in conjunction with macro-environmental factors.
By integrating these frameworks, businesses can gain a holistic view of their operating environment and develop robust strategies.
Conclusion
PEST Analysis is an essential framework for understanding the external factors shaping a business’s environment. By systematically evaluating Political, Economic, Social, and Technological influences, organizations can better anticipate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and craft resilient strategies.
Whether you’re launching a new product, entering a foreign market, or adapting to industry trends, PEST Analysis provides the macro-environmental insights needed for informed decision-making. Incorporate this tool into your strategic planning process and watch your business thrive in an ever-changing world.
Want to learn more about how strategic frameworks like PEST Analysis can transform your business? Explore other powerful tools and resources on ToolThinker.com and start making data-driven decisions today!